
National University of Singapore (NUS)
Ph.D. in Cyberspace Security
dong_ye_@outlook.com
Education


Experience




Honors & Awards
I am a Research Fellow at the School of Computing, National University of Singapore (NUS), hosted by Prof. Jin-Song Dong, and work closely with Prof. Tianwei Zhang from NTU. I received my Ph.D. in Cyberspace Security from the Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IIE, CAS) and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS), and my B.Eng. in Computer Science and Technologyfrom Shandong University.
My research focuses on practical cryptographic systems for secure and private AI, including secure multi-party computation, privacy-preserving machine learning, secure large language model inference, and system optimization. My work has been published in top-tier venues, including USENIX Security, ESORICS, ACSAC, PKC, PoPETs, ACNS, WWW, ICLR, NeurIPS, IEEE TIFS and TDSC, etc.
Research Interests: - Applied Cryptography - Secure Multi-Party Computation - Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "News
Research Highlights
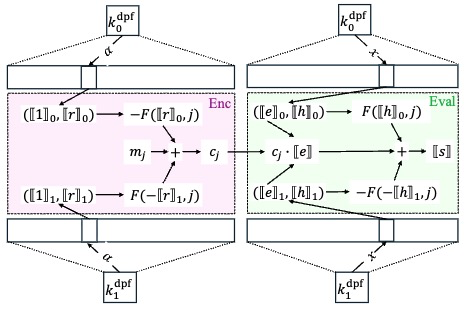
Streaming Function Secret Sharing and Its Applications
Xiangfu Song, Jianli Bai, Ye Dong†, Yijia Liu, Yu Zhang, Xianhui Lu, Tianwei Zhang
USENIX Security Symposium 2026
CCF-A CORE-A*
We introduce a new cryptographic primitive called streaming function secret sharing (SFSS), a new variant of FSS that is particularly suitable for secure computation over streaming messages. We formalize SFSS and propose concrete constructions, including SFSS for point functions, predicate functions, and feasibility results for generic functions. SFSS powers several promising applications in a simple and modular fashion, including conditional transciphering, policy-hiding aggregation, and attribute-hiding aggregation. In particular, our SFSS formalization and constructions identify security flaws and efficiency bottlenecks in existing solutions, and SFSS-powered solutions achieve the expected security goal with asymptotically and concretely better efficiency and/or enhanced functionality.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # streaming data aggregation
Streaming Function Secret Sharing and Its Applications
Xiangfu Song, Jianli Bai, Ye Dong†, Yijia Liu, Yu Zhang, Xianhui Lu, Tianwei Zhang
USENIX Security Symposium 2026 CCF-A CORE-A*
We introduce a new cryptographic primitive called streaming function secret sharing (SFSS), a new variant of FSS that is particularly suitable for secure computation over streaming messages. We formalize SFSS and propose concrete constructions, including SFSS for point functions, predicate functions, and feasibility results for generic functions. SFSS powers several promising applications in a simple and modular fashion, including conditional transciphering, policy-hiding aggregation, and attribute-hiding aggregation. In particular, our SFSS formalization and constructions identify security flaws and efficiency bottlenecks in existing solutions, and SFSS-powered solutions achieve the expected security goal with asymptotically and concretely better efficiency and/or enhanced functionality.
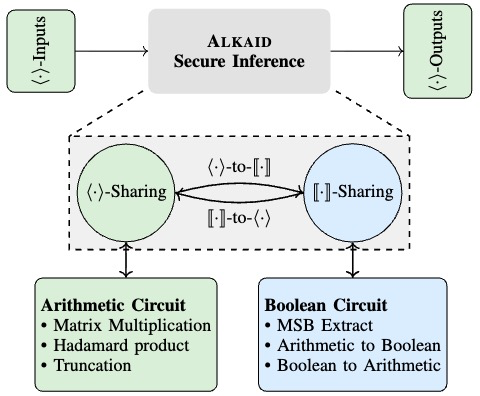
ALKAID: Accelerating Three-Party Boolean Circuits by Mixing Correlations and Redundancy
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song†, Yaxi Yang, Wen-jie Lu, Tianwei Zhang, Jianying Zhou, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
We propose a round-efficient 3PC framework ALKAID for Boolean circuits through improved multi-input AND gate. By mixing correlations and redundancy, we propose a concretely efficient correlation generation approach for small input bits $N\le 4$ and shift the correlation generation to the preprocessing phase. Building on this, we create a round-efficient AND protocol for general cases with $N>4$. Exploiting the improved multi-input AND gates, we design fast depth-optimized parallel prefix adder and share conversion primitives in 3PC, achieved with new techniques and optimizations for better concrete efficiency. We further apply these optimized primitives to enhance the efficiency of secure non-linear functions in machine learning.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # boolean circuits # machine learning
ALKAID: Accelerating Three-Party Boolean Circuits by Mixing Correlations and Redundancy
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song†, Yaxi Yang, Wen-jie Lu, Tianwei Zhang, Jianying Zhou, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
We propose a round-efficient 3PC framework ALKAID for Boolean circuits through improved multi-input AND gate. By mixing correlations and redundancy, we propose a concretely efficient correlation generation approach for small input bits $N\le 4$ and shift the correlation generation to the preprocessing phase. Building on this, we create a round-efficient AND protocol for general cases with $N>4$. Exploiting the improved multi-input AND gates, we design fast depth-optimized parallel prefix adder and share conversion primitives in 3PC, achieved with new techniques and optimizations for better concrete efficiency. We further apply these optimized primitives to enhance the efficiency of secure non-linear functions in machine learning.
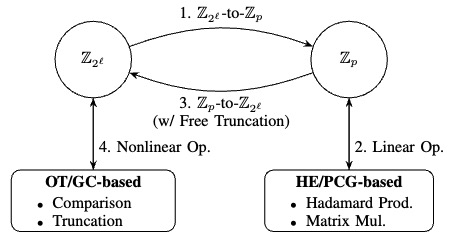
M&M: Secure Two-Party Machine Learning through Efficient Modulus Conversion and Mixed-Mode Protocols
Ye Dong, Wen-jie Lu†, Xiaoyang Hou, Kang Yang, Jian Liu
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
M&M features an efficient modulus conversion protocol. This breakthrough enables seamless integration of the most suitable cryptographic subprotocols within their optimal modulus domains, allowing linear computations to be executed over a prime modulus and nonlinear computations over a two-power modulus, with a minimal modulus conversion overhead. We further establish new benchmarks for the performance of fundamental primitives, namely comparison and multiplication, across various two-party techniques, together with our practical optimizations to improve efficiency.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # machine learning # homomorphic encryption
M&M: Secure Two-Party Machine Learning through Efficient Modulus Conversion and Mixed-Mode Protocols
Ye Dong, Wen-jie Lu†, Xiaoyang Hou, Kang Yang, Jian Liu
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
M&M features an efficient modulus conversion protocol. This breakthrough enables seamless integration of the most suitable cryptographic subprotocols within their optimal modulus domains, allowing linear computations to be executed over a prime modulus and nonlinear computations over a two-power modulus, with a minimal modulus conversion overhead. We further establish new benchmarks for the performance of fundamental primitives, namely comparison and multiplication, across various two-party techniques, together with our practical optimizations to improve efficiency.