Aritifical Intelligence (AI) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, yet their deployment in real-world systems fundamentally relies on centralized access to data and model internals. This assumption conflicts with practical requirements on data privacy, model confidentiality, and regulatory compliance.
In many realistic scenarios, data are distributed across multiple parties, highly sensitive, and cannot be directly shared. Meanwhile, AI-based services must operate under strict efficiency and safety constraints. Motivated by this gap, my research aims to build practical cryptographic systems that enable large-scale AI to be
2026
Streaming Function Secret Sharing and Its Applications
Xiangfu Song, Jianli Bai, Ye Dong†, Yijia Liu, Yu Zhang, Xianhui Lu, Tianwei Zhang
USENIX Security Symposium 2026
CCF-A CORE-A*
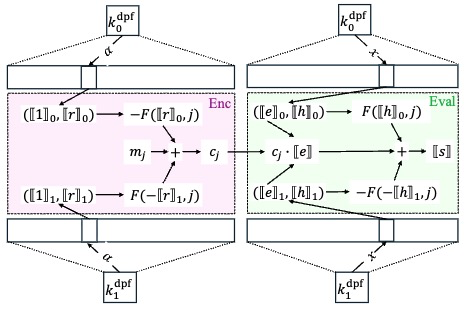
We introduce a new cryptographic primitive called streaming function secret sharing (SFSS), a new variant of FSS that is particularly suitable for secure computation over streaming messages. We formalize SFSS and propose concrete constructions, including SFSS for point functions, predicate functions, and feasibility results for generic functions. SFSS powers several promising applications in a simple and modular fashion, including conditional transciphering, policy-hiding aggregation, and attribute-hiding aggregation. In particular, our SFSS formalization and constructions identify security flaws and efficiency bottlenecks in existing solutions, and SFSS-powered solutions achieve the expected security goal with asymptotically and concretely better efficiency and/or enhanced functionality.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # streaming data aggregation
Streaming Function Secret Sharing and Its Applications
Xiangfu Song, Jianli Bai, Ye Dong†, Yijia Liu, Yu Zhang, Xianhui Lu, Tianwei Zhang
USENIX Security Symposium 2026 CCF-A CORE-A*
We introduce a new cryptographic primitive called streaming function secret sharing (SFSS), a new variant of FSS that is particularly suitable for secure computation over streaming messages. We formalize SFSS and propose concrete constructions, including SFSS for point functions, predicate functions, and feasibility results for generic functions. SFSS powers several promising applications in a simple and modular fashion, including conditional transciphering, policy-hiding aggregation, and attribute-hiding aggregation. In particular, our SFSS formalization and constructions identify security flaws and efficiency bottlenecks in existing solutions, and SFSS-powered solutions achieve the expected security goal with asymptotically and concretely better efficiency and/or enhanced functionality.
ChatIoT: Large Language Model-based Security Assistant for Internet of Things with RAG
Ye Dong†, Yan Lin Aung, Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Jianying Zhou
International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security 2026
CCF-C CORE-B
[TL;DR] [Paper] [LinkedIn] [SECGEEK]
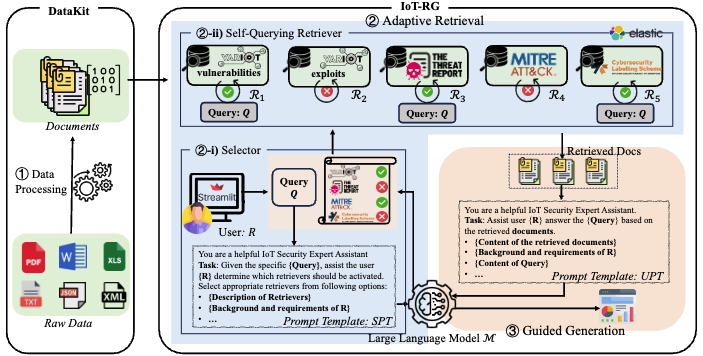
We propose CHATIOT, a large language model (LLM)-based IoT security assistant designed to disseminate IoT security and threat intelligence. By leveraging the versatile property of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), CHATIOT successfully integrates the advanced language understanding and reasoning capabilities of LLM with fast-evolving IoT security information. Moreover, we develop an end-to-end data processing toolkit to handle heterogeneous datasets. This toolkit converts datasets of various formats into retrievable documents and optimizes chunking strategies for efficient retrieval. Additionally, we define a set of common-use case specifications to guide the LLM in generating answers aligned with users' specific needs and expertise levels.
# large language models # IoT
ChatIoT: Large Language Model-based Security Assistant for Internet of Things with RAG
Ye Dong†, Yan Lin Aung, Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Jianying Zhou
International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security 2026 CCF-C CORE-B
We propose CHATIOT, a large language model (LLM)-based IoT security assistant designed to disseminate IoT security and threat intelligence. By leveraging the versatile property of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), CHATIOT successfully integrates the advanced language understanding and reasoning capabilities of LLM with fast-evolving IoT security information. Moreover, we develop an end-to-end data processing toolkit to handle heterogeneous datasets. This toolkit converts datasets of various formats into retrievable documents and optimizes chunking strategies for efficient retrieval. Additionally, we define a set of common-use case specifications to guide the LLM in generating answers aligned with users' specific needs and expertise levels.
SecP-Tuning: Efficient Privacy-Preserving Prompt Tuning for Large Language Models via MPC
Jinglong Luo, Zhuo Zhang, Yehong Zhang†, Shiyu Liu, Ye Dong, Xun Zhou†, Hui Wang, Yue Yu, Zenglin Xu†
International Conference on Learning Representations (arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.15307) 2026
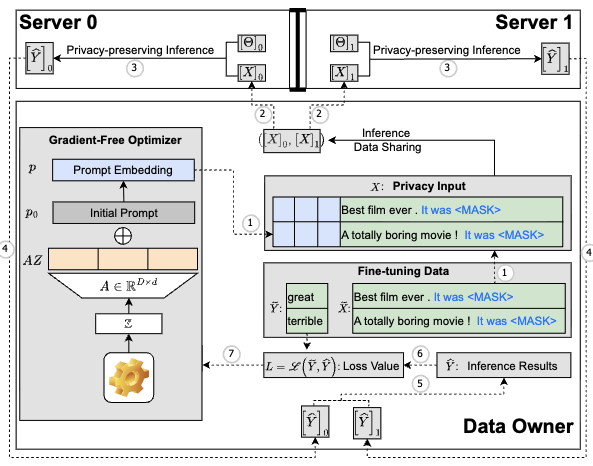
This paper identifies two primary obstacles to MPC-based privacy-preserving fine-tuning of LLMs: (1) the substantial computational overhead of backward and optimizer processes, and (2) the inefficiency of softmax-based attention mechanisms in MPC settings. To address these challenges, we propose SecFwT, the first MPC-based framework designed for efficient, privacy-preserving LLM fine-tuning. SecFwT introduces a forward-only tuning paradigm to eliminate backward and optimizer computations and employs MPC-friendly Random Feature Attention to approximate softmax attention, significantly reducing costly non-linear operations and computational complexity. Experimental results demonstrate that SecFwT delivers substantial improvements in efficiency and privacy preservation, enabling scalable and secure fine-tuning of LLMs for privacy-critical applications.
# secure multi-party computation # large languege models # fine-tuning
SecP-Tuning: Efficient Privacy-Preserving Prompt Tuning for Large Language Models via MPC
Jinglong Luo, Zhuo Zhang, Yehong Zhang†, Shiyu Liu, Ye Dong, Xun Zhou†, Hui Wang, Yue Yu, Zenglin Xu†
International Conference on Learning Representations (arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.15307) 2026
This paper identifies two primary obstacles to MPC-based privacy-preserving fine-tuning of LLMs: (1) the substantial computational overhead of backward and optimizer processes, and (2) the inefficiency of softmax-based attention mechanisms in MPC settings. To address these challenges, we propose SecFwT, the first MPC-based framework designed for efficient, privacy-preserving LLM fine-tuning. SecFwT introduces a forward-only tuning paradigm to eliminate backward and optimizer computations and employs MPC-friendly Random Feature Attention to approximate softmax attention, significantly reducing costly non-linear operations and computational complexity. Experimental results demonstrate that SecFwT delivers substantial improvements in efficiency and privacy preservation, enabling scalable and secure fine-tuning of LLMs for privacy-critical applications.
PRIVMARK: Private Large Language Models Watermarking with MPC
Thomas Fargues, Ye Dong†, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2026
CCF-C CORE-B
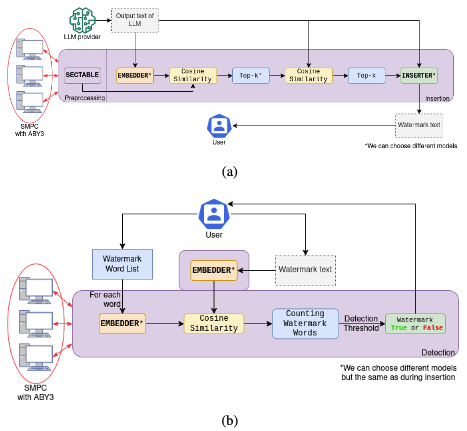
We investigate PostMark (EMNLP'2024), one of the state-of-the-art LLMs Watermarking methods, and formulate its basic operations. Then, we construct efficient protocols for these operations using the MPC primitives in a black-box manner. In this way, PRIVMARK enables multiple parties to collaboratively watermark an LLM's output without exposing the model's weights to any single computing party. We implement PRIVMARK using SecretFlow-SPU (USENIX ATC'2023) and evaluate its performance using the ABY3 (CCS'2018) backend. The experimental results show that PRIVMARK achieves semantically identical results compared to the plaintext baseline without MPC and is resistant against paraphrasing and removing attacks with reasonable efficiency.
# secure multi-party computation # large language models # watermarking
PRIVMARK: Private Large Language Models Watermarking with MPC
Thomas Fargues, Ye Dong†, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2026 CCF-C CORE-B
We investigate PostMark (EMNLP'2024), one of the state-of-the-art LLMs Watermarking methods, and formulate its basic operations. Then, we construct efficient protocols for these operations using the MPC primitives in a black-box manner. In this way, PRIVMARK enables multiple parties to collaboratively watermark an LLM's output without exposing the model's weights to any single computing party. We implement PRIVMARK using SecretFlow-SPU (USENIX ATC'2023) and evaluate its performance using the ABY3 (CCS'2018) backend. The experimental results show that PRIVMARK achieves semantically identical results compared to the plaintext baseline without MPC and is resistant against paraphrasing and removing attacks with reasonable efficiency.
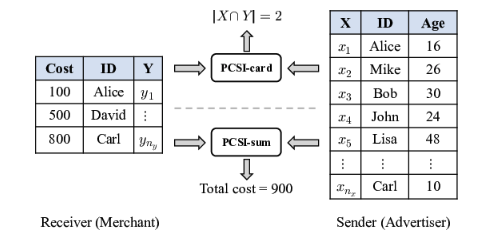
Fast Unbalanced Private Computation on Set Intersection from Permuted Multi-Query Private Membership Test
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Yaxi Yang, Qiang Liu
Cryptogtology ePrint Archive Under review. 2026
In this paper, we present a lightweight uPCSI framework with semi-honest security. First, we propose a permuted multi-query private membership test (pmqPMT) protocol and its labeled variant from the FHE-based PSI, thereby avoiding the costly comparison procedure. Upon our pmqPMT, we propose an optimized uPCSI framework for computing arbitrary functions over the intersection, along with several specific optimizations for better efficiency. Besides, our framework can be extended to support more comprehensive labeled uPCSI requirements, covering both single-labeled and double-labeled cases.
# Private Set Intersection # privacy # Permuted mqPMT
Fast Unbalanced Private Computation on Set Intersection from Permuted Multi-Query Private Membership Test
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Yaxi Yang, Qiang Liu
Cryptogtology ePrint ArchiveUnder review. 2026
In this paper, we present a lightweight uPCSI framework with semi-honest security. First, we propose a permuted multi-query private membership test (pmqPMT) protocol and its labeled variant from the FHE-based PSI, thereby avoiding the costly comparison procedure. Upon our pmqPMT, we propose an optimized uPCSI framework for computing arbitrary functions over the intersection, along with several specific optimizations for better efficiency. Besides, our framework can be extended to support more comprehensive labeled uPCSI requirements, covering both single-labeled and double-labeled cases.
2025
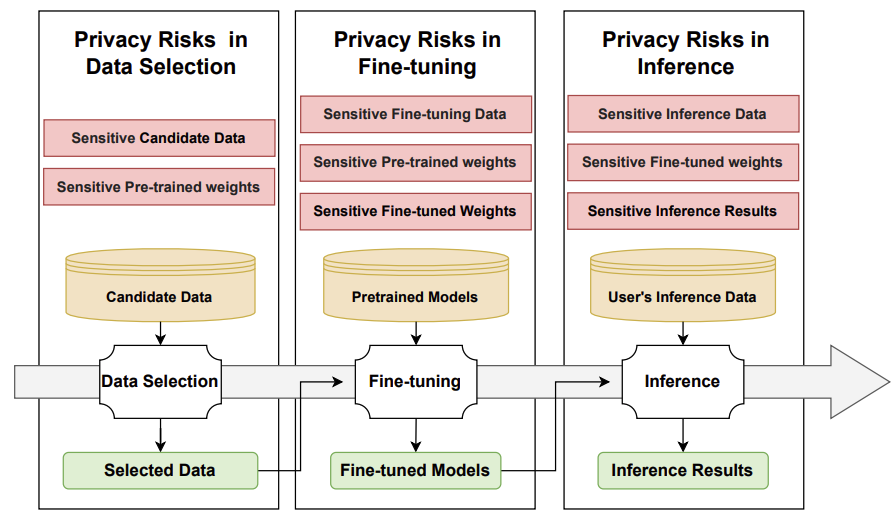
Cryptography-based privacy-preserving large language models: a lifecycle survey of frameworks, methods, and future directions
Jinglong Luo, Yehong Zhang, Zhuo Zhang, Shiyu Liu, Ye Dong, Haoran Li, Yue Yu, Hui Wang, Xun Zhou†, Zenglin Xu
Artificial Intelligence Review 2025
Survey
We provide a comprehensive review of existing CPLMs research and systematically classifies them, enabling researchers to effectively coordinate optimization strategies for the efficient design of CPLMs algorithms. Finally, based on the limitations of current CPLMs research, we outline several promising directions for future exploration.
# secure multi-party computation # large language models # survey
Cryptography-based privacy-preserving large language models: a lifecycle survey of frameworks, methods, and future directions
Jinglong Luo, Yehong Zhang, Zhuo Zhang, Shiyu Liu, Ye Dong, Haoran Li, Yue Yu, Hui Wang, Xun Zhou†, Zenglin Xu
Artificial Intelligence Review 2025 Survey
We provide a comprehensive review of existing CPLMs research and systematically classifies them, enabling researchers to effectively coordinate optimization strategies for the efficient design of CPLMs algorithms. Finally, based on the limitations of current CPLMs research, we outline several promising directions for future exploration.
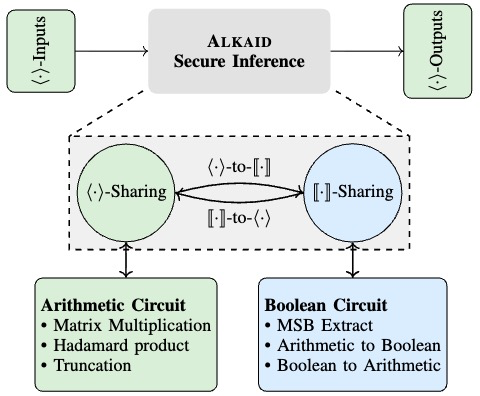
ALKAID: Accelerating Three-Party Boolean Circuits by Mixing Correlations and Redundancy
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song†, Yaxi Yang, Wen-jie Lu, Tianwei Zhang, Jianying Zhou, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
We propose a round-efficient 3PC framework ALKAID for Boolean circuits through improved multi-input AND gate. By mixing correlations and redundancy, we propose a concretely efficient correlation generation approach for small input bits $N\le 4$ and shift the correlation generation to the preprocessing phase. Building on this, we create a round-efficient AND protocol for general cases with $N>4$. Exploiting the improved multi-input AND gates, we design fast depth-optimized parallel prefix adder and share conversion primitives in 3PC, achieved with new techniques and optimizations for better concrete efficiency. We further apply these optimized primitives to enhance the efficiency of secure non-linear functions in machine learning.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # boolean circuits # machine learning
ALKAID: Accelerating Three-Party Boolean Circuits by Mixing Correlations and Redundancy
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song†, Yaxi Yang, Wen-jie Lu, Tianwei Zhang, Jianying Zhou, Jin-Song Dong
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
We propose a round-efficient 3PC framework ALKAID for Boolean circuits through improved multi-input AND gate. By mixing correlations and redundancy, we propose a concretely efficient correlation generation approach for small input bits $N\le 4$ and shift the correlation generation to the preprocessing phase. Building on this, we create a round-efficient AND protocol for general cases with $N>4$. Exploiting the improved multi-input AND gates, we design fast depth-optimized parallel prefix adder and share conversion primitives in 3PC, achieved with new techniques and optimizations for better concrete efficiency. We further apply these optimized primitives to enhance the efficiency of secure non-linear functions in machine learning.
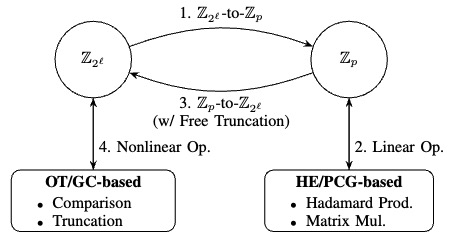
M&M: Secure Two-Party Machine Learning through Efficient Modulus Conversion and Mixed-Mode Protocols
Ye Dong, Wen-jie Lu†, Xiaoyang Hou, Kang Yang, Jian Liu
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
M&M features an efficient modulus conversion protocol. This breakthrough enables seamless integration of the most suitable cryptographic subprotocols within their optimal modulus domains, allowing linear computations to be executed over a prime modulus and nonlinear computations over a two-power modulus, with a minimal modulus conversion overhead. We further establish new benchmarks for the performance of fundamental primitives, namely comparison and multiplication, across various two-party techniques, together with our practical optimizations to improve efficiency.
# secure multi-party computation # applied cryptography # machine learning # homomorphic encryption
M&M: Secure Two-Party Machine Learning through Efficient Modulus Conversion and Mixed-Mode Protocols
Ye Dong, Wen-jie Lu†, Xiaoyang Hou, Kang Yang, Jian Liu
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
M&M features an efficient modulus conversion protocol. This breakthrough enables seamless integration of the most suitable cryptographic subprotocols within their optimal modulus domains, allowing linear computations to be executed over a prime modulus and nonlinear computations over a two-power modulus, with a minimal modulus conversion overhead. We further establish new benchmarks for the performance of fundamental primitives, namely comparison and multiplication, across various two-party techniques, together with our practical optimizations to improve efficiency.
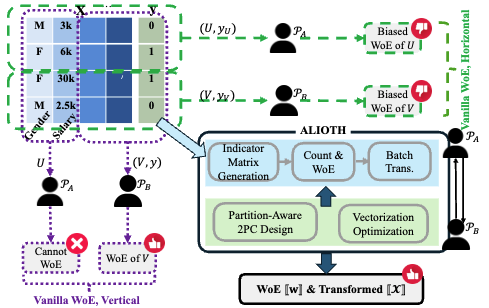
ALIOTH: An Efficient and Secure Weight-of-Evidence Framework for Privacy-Preserving Data Processing
Ye Dong, Xiangfu Song†, Wj Lu, Xudong Chen, Yaxi Yang, Ruonan Chen, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
Cryptology ePrint Archive Under review. 2025
In this work, we present ALIOTH, an efficient 2PC framework that securely transforms raw categorical and numerical features into Weight-of-Evidence (WoE)-based numerical representations under both vertical and horizontal data partitions. By incorporating our proposed partition-aware 2PC protocols and vectorization optimizations, ALIOTH efficiently generates WoE-transformed datasets in secret. To demonstrate scalability, we conduct experiments on diverse datasets. Notably, ALIOTH can transform 3 million data samples with 100 features securely within half an hour over a wide-area network. Furthermore, ALIOTH can be seamlessly integrated with existing 2PC-based ML frameworks. Empirical evaluations on real-world financial datasets show ALIOTH improves both the predictive performance of logistic regression and 2PC training efficiency.
# secure multi-party computation # Weight-of-Evidence
ALIOTH: An Efficient and Secure Weight-of-Evidence Framework for Privacy-Preserving Data Processing
Ye Dong, Xiangfu Song†, Wj Lu, Xudong Chen, Yaxi Yang, Ruonan Chen, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
Cryptology ePrint ArchiveUnder review. 2025
In this work, we present ALIOTH, an efficient 2PC framework that securely transforms raw categorical and numerical features into Weight-of-Evidence (WoE)-based numerical representations under both vertical and horizontal data partitions. By incorporating our proposed partition-aware 2PC protocols and vectorization optimizations, ALIOTH efficiently generates WoE-transformed datasets in secret. To demonstrate scalability, we conduct experiments on diverse datasets. Notably, ALIOTH can transform 3 million data samples with 100 features securely within half an hour over a wide-area network. Furthermore, ALIOTH can be seamlessly integrated with existing 2PC-based ML frameworks. Empirical evaluations on real-world financial datasets show ALIOTH improves both the predictive performance of logistic regression and 2PC training efficiency.
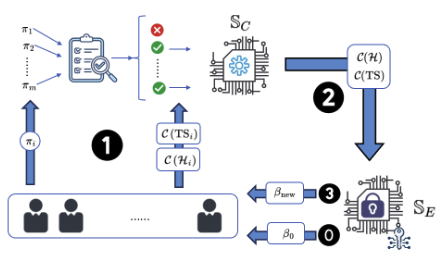
ByzSFL: Achieving Byzantine-Robust Secure Federated Learning with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Yongming Fan, Rui Zhu, Zihao Wang, Chenghong Wang, Haixu Tang, Ye Dong, Hyunghoon Cho, Lucila Ohno-Machado
arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.06953 Under review. 2025
We propose ByzSFL, a novel SFL system that achieves Byzantine-robust secure aggregation with high efficiency. Our approach offloads aggregation weight calculations to individual parties and introduces a practical zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) protocol toolkit. This toolkit supports widely used operators for calculating aggregation weights, ensuring correct computations without compromising data privacy. Not only does this method maintain aggregation integrity, but it also significantly boosts computational efficiency, making ByzSFL approximately 100 times faster than existing solutions. Furthermore, our method aligns with open-source AI trends, enabling plaintext publication of the final model without additional information leakage, thereby enhancing the practicality and robustness of SFL in real-world applications.
# federated learning # Byzantine-robustness # zero-knowledge proofs # homomomrphic encryption
ByzSFL: Achieving Byzantine-Robust Secure Federated Learning with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Yongming Fan, Rui Zhu, Zihao Wang, Chenghong Wang, Haixu Tang, Ye Dong, Hyunghoon Cho, Lucila Ohno-Machado
arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.06953Under review. 2025
We propose ByzSFL, a novel SFL system that achieves Byzantine-robust secure aggregation with high efficiency. Our approach offloads aggregation weight calculations to individual parties and introduces a practical zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) protocol toolkit. This toolkit supports widely used operators for calculating aggregation weights, ensuring correct computations without compromising data privacy. Not only does this method maintain aggregation integrity, but it also significantly boosts computational efficiency, making ByzSFL approximately 100 times faster than existing solutions. Furthermore, our method aligns with open-source AI trends, enabling plaintext publication of the final model without additional information leakage, thereby enhancing the practicality and robustness of SFL in real-world applications.
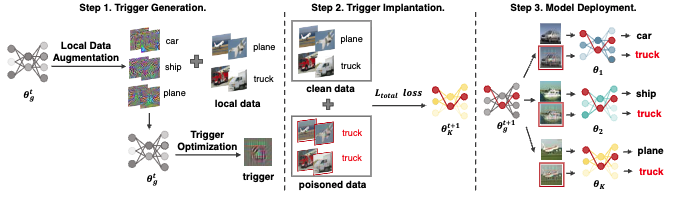
Practical and General Backdoor Attacks Against Personalized Federated Learning
Yuexin Xuan, Xiaojun Chen†, Zhendong Zhao, Ye Dong, Xin Zhao, Bisheng Tang
International Conference on Neural Information Processing 2025
CCF-C CORE-B
Unlike traditional FL, PFL is considered more robust against backdoor attacks due to two inherent properties: (P1) Heterogeneous data distribution mitigates the impact of poisoned neurons during aggregation, and (P2) Locally personalized fine-tuning further modifies poisoned neurons to fit local data distributions, disrupting the linkage between the trigger and attack target. However, we reveal that attackers can exploit deeper insights to bypass these properties and propose a new attack method called BadPFL. For P1, BadPFL reduces the trigger’s dependence on poisoned neurons by integrating target semantic information directly into it, ensuring that even benign models can naturally associate the trigger with the target class, thus enabling the backdoor to survive during aggregation. For P2, we enhance the attack’s persistence by integrating more robust target features, making it more resistant to modifications introduced by local fine-tuning. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that BadPFL remains highly effective against various PFL methods, even in the presence of advanced defense strategies.
# backdoor # federated learning
Practical and General Backdoor Attacks Against Personalized Federated Learning
Yuexin Xuan, Xiaojun Chen†, Zhendong Zhao, Ye Dong, Xin Zhao, Bisheng Tang
International Conference on Neural Information Processing 2025 CCF-C CORE-B
Unlike traditional FL, PFL is considered more robust against backdoor attacks due to two inherent properties: (P1) Heterogeneous data distribution mitigates the impact of poisoned neurons during aggregation, and (P2) Locally personalized fine-tuning further modifies poisoned neurons to fit local data distributions, disrupting the linkage between the trigger and attack target. However, we reveal that attackers can exploit deeper insights to bypass these properties and propose a new attack method called BadPFL. For P1, BadPFL reduces the trigger’s dependence on poisoned neurons by integrating target semantic information directly into it, ensuring that even benign models can naturally associate the trigger with the target class, thus enabling the backdoor to survive during aggregation. For P2, we enhance the attack’s persistence by integrating more robust target features, making it more resistant to modifications introduced by local fine-tuning. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that BadPFL remains highly effective against various PFL methods, even in the presence of advanced defense strategies.
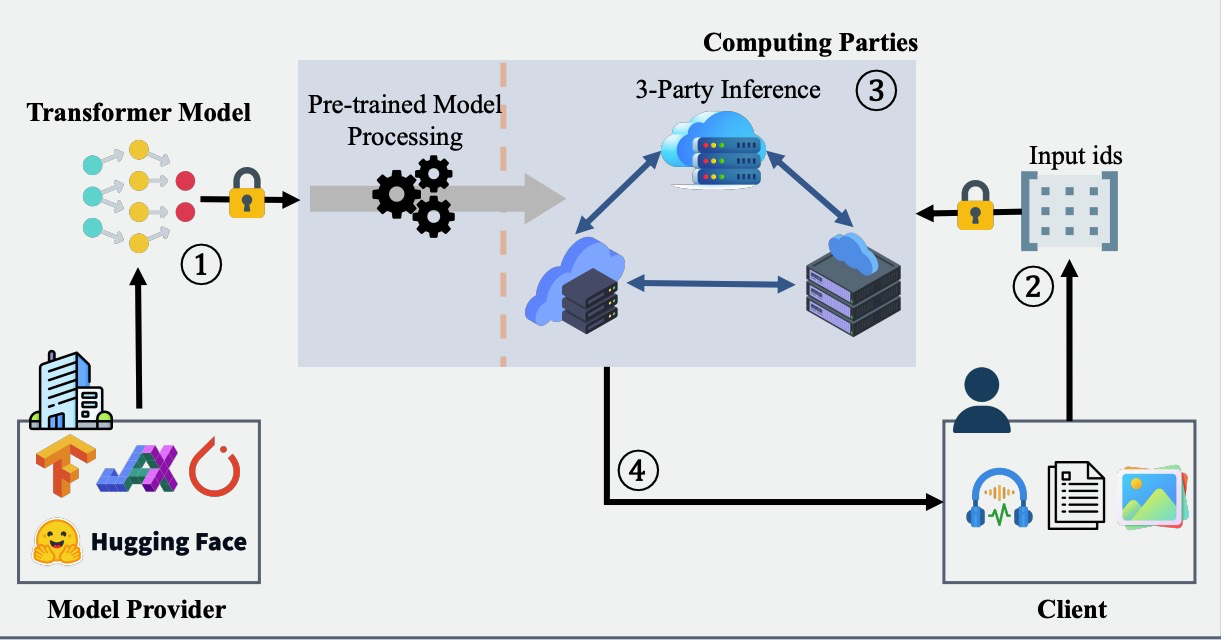
PUMA: Secure Inference of LLaMA-7B in Five Minutes
Ye Dong, Wen-Jie Lu, Yancheng Zheng, Haoqi Wu, Derun Zhao, Jin Tan, Zhicong Huang, Cheng Hong†, Tao Wei, Wen-Guang Chen, Jianying Zhou
Security and Safety
[TL;DR] [Paper] [Code] [JIQIZHIXIN]
we propose an MPC framework PUMA to enable secure and efficient Transformer model inference. We first design high-quality approximations for the bottleneck functions in Transformers such as GELU and Softmax, reducing about 20 − 76% computation and communication costs than state-of-the-art works without performance drop. Then, we provide concrete instantiations for secure Embedding and LayerNorm. These implementations produce correct results and integrate compatible system architectures of cleartext Transformer models. Finally, we conducted extensive experiments on six popular benchmarks: text classification/generation/summarization/translation, audio-to-text, and image-to-text. Results show that PUMA can finish most tasks in several minutes, with comparable model performance (e.g., accuracy) as cleartext, and even evaluate LLaMA-7B in less than 5 minutes to generate 1 token.
# secure multi-party computation # large language models
PUMA: Secure Inference of LLaMA-7B in Five Minutes
Ye Dong, Wen-Jie Lu, Yancheng Zheng, Haoqi Wu, Derun Zhao, Jin Tan, Zhicong Huang, Cheng Hong†, Tao Wei, Wen-Guang Chen, Jianying Zhou
Security and Safety
we propose an MPC framework PUMA to enable secure and efficient Transformer model inference. We first design high-quality approximations for the bottleneck functions in Transformers such as GELU and Softmax, reducing about 20 − 76% computation and communication costs than state-of-the-art works without performance drop. Then, we provide concrete instantiations for secure Embedding and LayerNorm. These implementations produce correct results and integrate compatible system architectures of cleartext Transformer models. Finally, we conducted extensive experiments on six popular benchmarks: text classification/generation/summarization/translation, audio-to-text, and image-to-text. Results show that PUMA can finish most tasks in several minutes, with comparable model performance (e.g., accuracy) as cleartext, and even evaluate LLaMA-7B in less than 5 minutes to generate 1 token.
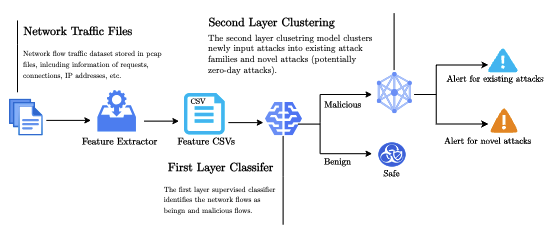
LAPIS: Layered Anomaly Detection System for IoT Security
Cheng Wang*, Yan Lin Aung*†, Ye Dong, Trupil Limbasiya, Jianying Zhou
Applied Cryptography and Network Security Workshops 2025
In this paper, we present an anomaly detection system that has been integrated with a honeypot infrastructure to facilitate real-time data capture and anomaly detection. The two-layer anomaly detection system, named LAPIS, is capable of detecting malicious network traffic and identifying novel attacks. This integration aims to enhance security measures by providing a sophisticated mechanism for monitoring and analyzing network flows with precision and efficiency. We evaluated LAPIS using realistic network traffic collected by the honeypot during 12 months of operation. The experimental results show that the overall F1 score of LAPIS reaches 0.91 and 0.84 for detecting malicious network flows and zero-day attacks, respectively outperforming the closest state-of-the-art work. Compared to VirusTotal, which analyzes suspicious files and URLs to detect malware and malicious content, 61% of novel attacks are detected earlier by our system or yet to be available in VirusTotal.
# anomaly detection # IoT security
LAPIS: Layered Anomaly Detection System for IoT Security
Cheng Wang*, Yan Lin Aung*†, Ye Dong, Trupil Limbasiya, Jianying Zhou
Applied Cryptography and Network Security Workshops 2025
In this paper, we present an anomaly detection system that has been integrated with a honeypot infrastructure to facilitate real-time data capture and anomaly detection. The two-layer anomaly detection system, named LAPIS, is capable of detecting malicious network traffic and identifying novel attacks. This integration aims to enhance security measures by providing a sophisticated mechanism for monitoring and analyzing network flows with precision and efficiency. We evaluated LAPIS using realistic network traffic collected by the honeypot during 12 months of operation. The experimental results show that the overall F1 score of LAPIS reaches 0.91 and 0.84 for detecting malicious network flows and zero-day attacks, respectively outperforming the closest state-of-the-art work. Compared to VirusTotal, which analyzes suspicious files and URLs to detect malware and malicious content, 61% of novel attacks are detected earlier by our system or yet to be available in VirusTotal.
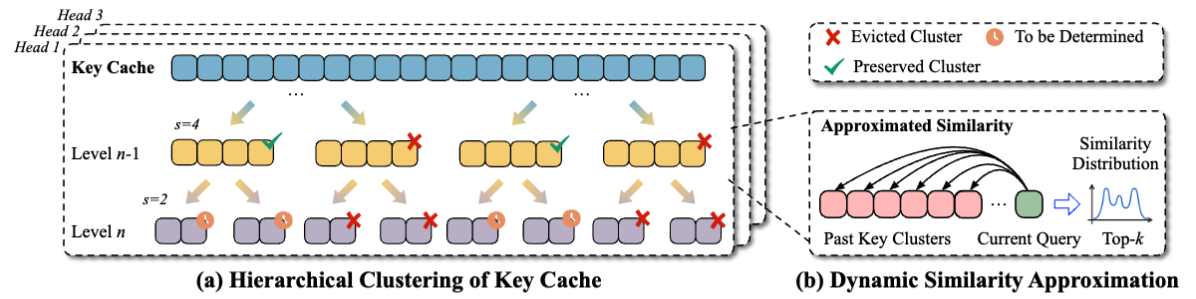
MPCache: MPC-Friendly KV Cache Eviction for Efficient Private LLM Inference
Wenxuan Zeng, Ye Dong, Jinjin Zhou, Jin Tan, Lei Wang, Tao Wei, Runsheng Wang, Meng Li†
Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2025
CCF-A CORE-A*
[TL;DR] [Paper] [Code] [Video]
We propose AttentiveNAS that focuses on improving the sampling strategy to achieve better performance Pareto. We also propose algorithms to efficiently and effectively identify the networks on the Pareto during training. Without extra re-training or post-processing, we can simultaneously obtain a large number of networks across a wide range of FLOPs. Our discovered model family, AttentiveNAS models, achieves top-1 accuracy from 77.3% to 80.7% on ImageNet, and outperforms SOTA models, including BigNAS and Once-for-All networks. We also achieve ImageNet accuracy of 80.1% with only 491 MFLOPs.
# secure multi-party computation # large language models # KV Cache
MPCache: MPC-Friendly KV Cache Eviction for Efficient Private LLM Inference
Wenxuan Zeng, Ye Dong, Jinjin Zhou, Jin Tan, Lei Wang, Tao Wei, Runsheng Wang, Meng Li†
Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2025 CCF-A CORE-A*
We propose AttentiveNAS that focuses on improving the sampling strategy to achieve better performance Pareto. We also propose algorithms to efficiently and effectively identify the networks on the Pareto during training. Without extra re-training or post-processing, we can simultaneously obtain a large number of networks across a wide range of FLOPs. Our discovered model family, AttentiveNAS models, achieves top-1 accuracy from 77.3% to 80.7% on ImageNet, and outperforms SOTA models, including BigNAS and Once-for-All networks. We also achieve ImageNet accuracy of 80.1% with only 491 MFLOPs.
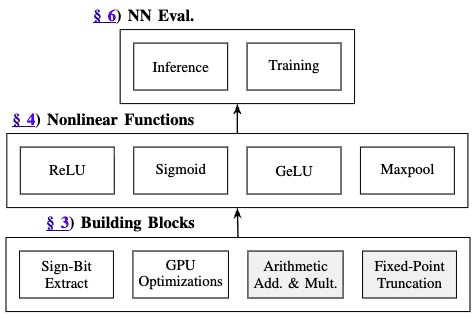
MIZAR: Boosting Secure Three-Party Deep Learning with Co-Designed Sign-Bit Extraction and GPU Acceleration
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song, Yaxi Yang†, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference 2025
CCF-B CORE-A
[TL;DR] [Paper] [Sldie] [Code]
We propose an optimized constant-round secure Sign-Bit Extraction protocol with communication and GPU-specific optimizations. Concretely, we construct a new masked randomized list by exploiting the upper bound of bit-wise prefix-sum to reduce online communication by up to $50\%$, and integrate fast modular-reduction and kernel fusion techniques to enhance GPU utilization in MPC protocols. Besides, we propose specific optimizations for secure piecewise polynomial approximations and Maxpool computation in neural network evaluations.
# secure multi-party computation # secret sharing # GPU
MIZAR: Boosting Secure Three-Party Deep Learning with Co-Designed Sign-Bit Extraction and GPU Acceleration
Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Xiangfu Song, Yaxi Yang†, Tianwei Zhang, Jin-Song Dong
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference 2025 CCF-B CORE-A
We propose an optimized constant-round secure Sign-Bit Extraction protocol with communication and GPU-specific optimizations. Concretely, we construct a new masked randomized list by exploiting the upper bound of bit-wise prefix-sum to reduce online communication by up to $50\%$, and integrate fast modular-reduction and kernel fusion techniques to enhance GPU utilization in MPC protocols. Besides, we propose specific optimizations for secure piecewise polynomial approximations and Maxpool computation in neural network evaluations.
XGT: Fast and Secure Decision Tree Training and Inference on GPUs
Qifan Wang, Shujie Cui†, Lei Zhou, Ye Dong, Jianli Bai, Yun Sing Koh, Giovanni Russello
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
We introduce the eXpress GPU-based Tree (XGT), a fast MPC-based framework for private DT training and inference on GPUs. XGTconverts the majority of operations in training and inference into parallelizable matrix operations, supplemented by various optimizations, including matrix dimension reductions. This innovative design leads to substantial reductions in communication overhead while maintaining the critical property of obliviousness. XGTalso achieves a stronger security guarantee, where all data items, the tree shape, access patterns, and data distributions generated during the training and inference are protected. XGTonly reveals the tree depth.
# secure multi-party computation # decision tree # GPU
XGT: Fast and Secure Decision Tree Training and Inference on GPUs
Qifan Wang, Shujie Cui†, Lei Zhou, Ye Dong, Jianli Bai, Yun Sing Koh, Giovanni Russello
IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
We introduce the eXpress GPU-based Tree (XGT), a fast MPC-based framework for private DT training and inference on GPUs. XGTconverts the majority of operations in training and inference into parallelizable matrix operations, supplemented by various optimizations, including matrix dimension reductions. This innovative design leads to substantial reductions in communication overhead while maintaining the critical property of obliviousness. XGTalso achieves a stronger security guarantee, where all data items, the tree shape, access patterns, and data distributions generated during the training and inference are protected. XGTonly reveals the tree depth.
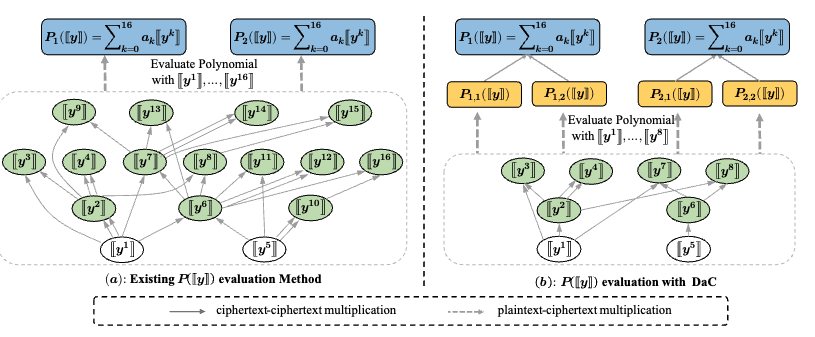
JAGUAR: Efficient and Secure Unbalanced PSI under Malicious Adversaries in the Client-Server Setting
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Qiang Liu, Tingyu Fan
Cybersecurity 2025
we present JAGUAR, a maliciously secure and efficient uPSI protocol designed for this setting. JAGUAR reduces online computation through a Divide-and-Combine optimization, requiring only $O(\sqrt{|X|})$ homomorphic multiplications. Furthermore, it employs a novel fixed VOLE-based OPRF that enables reusable and lightweight pre-processing across multiple clients.
# private set intersection # OPRF
JAGUAR: Efficient and Secure Unbalanced PSI under Malicious Adversaries in the Client-Server Setting
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Qiang Liu, Tingyu Fan
Cybersecurity 2025
we present JAGUAR, a maliciously secure and efficient uPSI protocol designed for this setting. JAGUAR reduces online computation through a Divide-and-Combine optimization, requiring only $O(\sqrt{|X|})$ homomorphic multiplications. Furthermore, it employs a novel fixed VOLE-based OPRF that enables reusable and lightweight pre-processing across multiple clients.
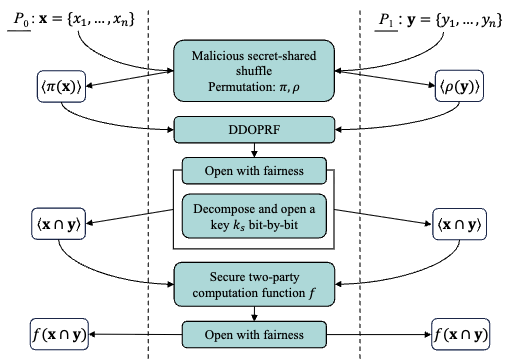
Maliciously Secure Circuit Private Set Intersection via SPDZ-Compatible Oblivious PRF
Yaxi Yang, Xiaojian Liang, Xiangfu Song†, Ye Dong, Linting Huang, Hongyu Ren, Changyu Dong†, Jianying Zhou
Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies 2025
CCF-C CORE-A
This paper tackles the previously mentioned issue by presenting the first maliciously secure Circuit-PSI protocol. Our key innovation, the Distributed Dual-key Oblivious Pseudorandom Function (DDOPRF), enables the oblivious evaluation of secret-shared inputs using dual keys within the SPDZ MPC framework. Notably, this construction seamlessly ensures fairness within the Circuit-PSI. Compared to the state-of-the-art semi-honest Circuit-PSI protocol (PoPETS'22), experimental results demonstrate that our malicious Circuit-PSI protocol not only reduces around 5x communication costs but also enhances efficiency, particularly for modest input sets ($\le 2^{14}$) in the case of the WAN setting with high latency and limited bandwidth.
# private set intersection # secret sharing # applied cryptography
Maliciously Secure Circuit Private Set Intersection via SPDZ-Compatible Oblivious PRF
Yaxi Yang, Xiaojian Liang, Xiangfu Song†, Ye Dong, Linting Huang, Hongyu Ren, Changyu Dong†, Jianying Zhou
Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies 2025 CCF-C CORE-A
This paper tackles the previously mentioned issue by presenting the first maliciously secure Circuit-PSI protocol. Our key innovation, the Distributed Dual-key Oblivious Pseudorandom Function (DDOPRF), enables the oblivious evaluation of secret-shared inputs using dual keys within the SPDZ MPC framework. Notably, this construction seamlessly ensures fairness within the Circuit-PSI. Compared to the state-of-the-art semi-honest Circuit-PSI protocol (PoPETS'22), experimental results demonstrate that our malicious Circuit-PSI protocol not only reduces around 5x communication costs but also enhances efficiency, particularly for modest input sets ($\le 2^{14}$) in the case of the WAN setting with high latency and limited bandwidth.
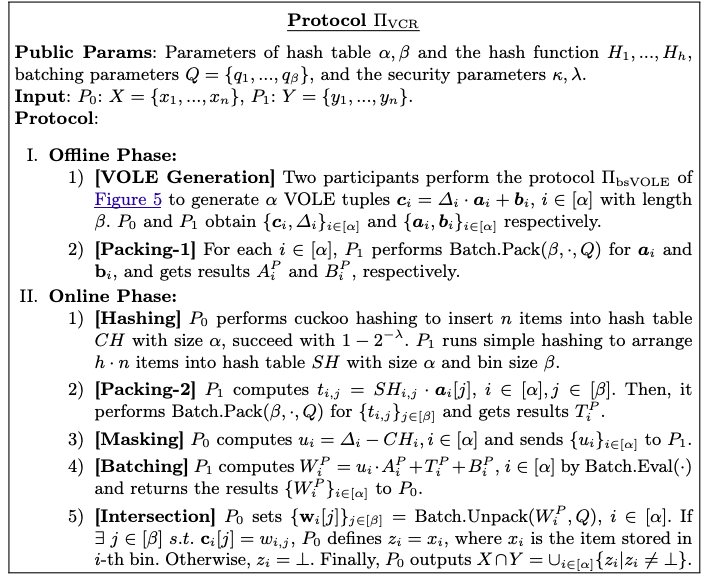
VCR: Fast Private Set Intersection with Improved VOLE and CRT-Batching
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Yaxi Yang, Qiang Liu
IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications 2025
CCF-C CORE-B
In this paper, we propose VCR, an efficient PSI protocol from vector OLE (VOLE) with the offline-online paradigm. Concretely, we first propose the batched short VOLE protocol to reduce offline overhead for generating VOLE tuples. Experiments demonstrate that VCR outperforms prior art. Then, we design a batched private membership test protocol from pre-computed VOLE to accelerate the online computation.
# private set intersection # VOLE # CRT
VCR: Fast Private Set Intersection with Improved VOLE and CRT-Batching
Weizhan Jing, Xiaojun Chen, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Yaxi Yang, Qiang Liu
IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications 2025 CCF-C CORE-B
In this paper, we propose VCR, an efficient PSI protocol from vector OLE (VOLE) with the offline-online paradigm. Concretely, we first propose the batched short VOLE protocol to reduce offline overhead for generating VOLE tuples. Experiments demonstrate that VCR outperforms prior art. Then, we design a batched private membership test protocol from pre-computed VOLE to accelerate the online computation.
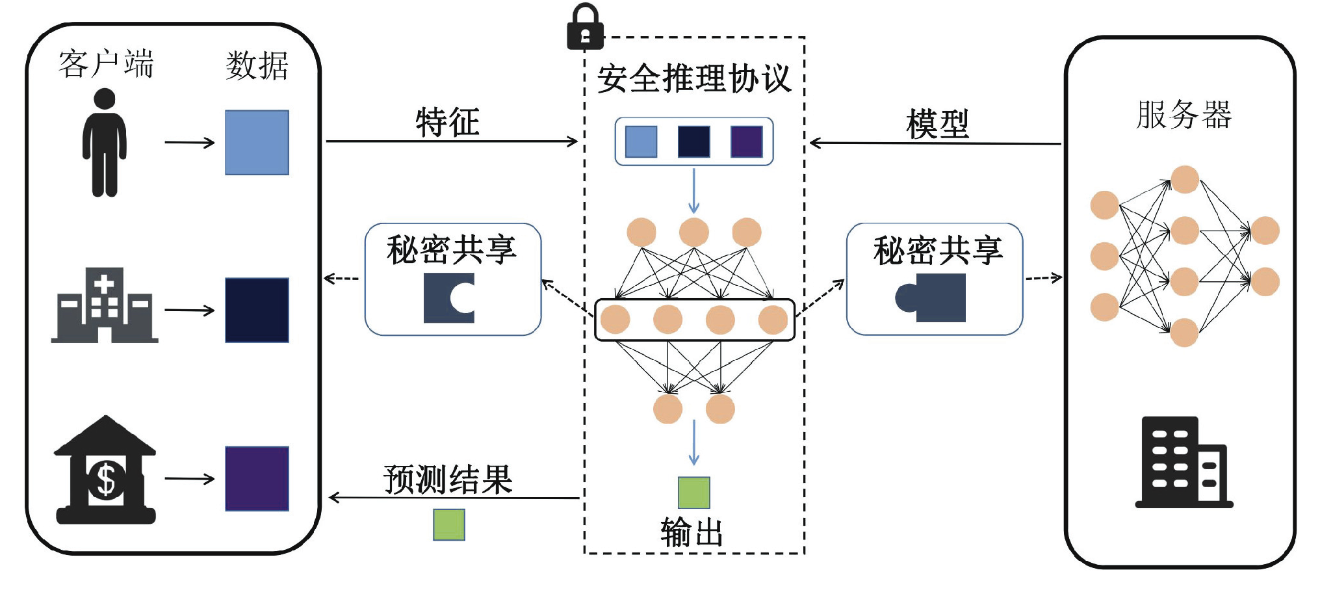
Multi-Party Collaborative Secure Inference Protocols for Vertically Distributed Feature Scenarios
Tao Tang, Haixia Xu†, Ye Dong, Yinchang Zhou, Jinling Tang
Journal of Cyber Security 2025
his paper introduces VSecNN, a cooperative neural network inference protocol executed by a single server and multiple clients. For linear layers, the protocol employs homomor-phic encryption to facilitate efficient matrix multiplication, while for non-linear layers, it integrates garbled circuits and oblivious transfer techniques to securely compute activation functions, with each layer’s results securely shared be-tween the client and server via additive secret sharing. The protocol adheres to a two-phase paradigm that is relatively independent, concentrating the bulk of computational costs in an input-independent preprocessing stage, with the online phase necessitating only two rounds of interaction: one for the input of masked features and another for the output of inference results. Comparative experiments demonstrate that VSecNN significantly enhances efficiency and stability in the collaborative inference process within vertically distributed feature scenarios, while substantially reducing system communication overhead and resource utilization
# secure multi-party computation # neural network
Multi-Party Collaborative Secure Inference Protocols for Vertically Distributed Feature Scenarios
Tao Tang, Haixia Xu†, Ye Dong, Yinchang Zhou, Jinling Tang
Journal of Cyber Security 2025
his paper introduces VSecNN, a cooperative neural network inference protocol executed by a single server and multiple clients. For linear layers, the protocol employs homomor-phic encryption to facilitate efficient matrix multiplication, while for non-linear layers, it integrates garbled circuits and oblivious transfer techniques to securely compute activation functions, with each layer’s results securely shared be-tween the client and server via additive secret sharing. The protocol adheres to a two-phase paradigm that is relatively independent, concentrating the bulk of computational costs in an input-independent preprocessing stage, with the online phase necessitating only two rounds of interaction: one for the input of masked features and another for the output of inference results. Comparative experiments demonstrate that VSecNN significantly enhances efficiency and stability in the collaborative inference process within vertically distributed feature scenarios, while substantially reducing system communication overhead and resource utilization
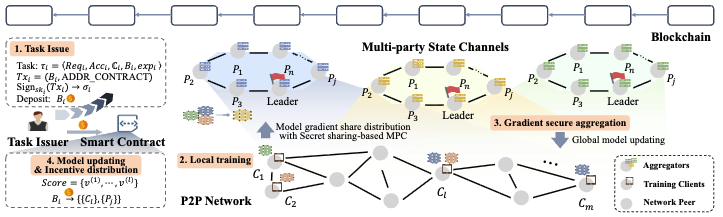
FLock: Robust and Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning based on Practical Blockchain State Channels
Ruonan Chen, Ye Dong, Yizhong Liu, Tingyu Fan, Dawei Liu, Zhenyu Guan, Jianwei Liu, Jianying Zhou
ACM on Web Conference 2025
CCF-A CORE-A*
We propose FLock, a robust and privacy-preserving FL scheme based on practical blockchain state channels. First, we propose a lightweight secure Multi-party Computation (MPC)-friendly robust aggregation method through quantization, median, and Hamming distance, which could resist poisoning attacks against up to <50% malicious clients. Besides, we propose communication-efficient Shamir's secret sharing-based MPC protocols to protect data privacy with high model accuracy. Second, we utilize blockchain off-chain state channels to achieve immutable model records and incentive distribution. FLock achieves cost-effective compatibility with practical cryptocurrency platforms, e.g. Ethereum, along with fair incentives, by merging the secure aggregation into a multi-party state channel. In addition, a pipelined Byzantine Fault-Tolerant (BFT) consensus is integrated where each aggregator can reconstruct the final aggregated results.
# secure multi-party computation # federated learning # blockchain # robustness
FLock: Robust and Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning based on Practical Blockchain State Channels
Ruonan Chen, Ye Dong, Yizhong Liu, Tingyu Fan, Dawei Liu, Zhenyu Guan, Jianwei Liu, Jianying Zhou
ACM on Web Conference 2025 CCF-A CORE-A*
We propose FLock, a robust and privacy-preserving FL scheme based on practical blockchain state channels. First, we propose a lightweight secure Multi-party Computation (MPC)-friendly robust aggregation method through quantization, median, and Hamming distance, which could resist poisoning attacks against up to <50% malicious clients. Besides, we propose communication-efficient Shamir's secret sharing-based MPC protocols to protect data privacy with high model accuracy. Second, we utilize blockchain off-chain state channels to achieve immutable model records and incentive distribution. FLock achieves cost-effective compatibility with practical cryptocurrency platforms, e.g. Ethereum, along with fair incentives, by merging the secure aggregation into a multi-party state channel. In addition, a pipelined Byzantine Fault-Tolerant (BFT) consensus is integrated where each aggregator can reconstruct the final aggregated results.
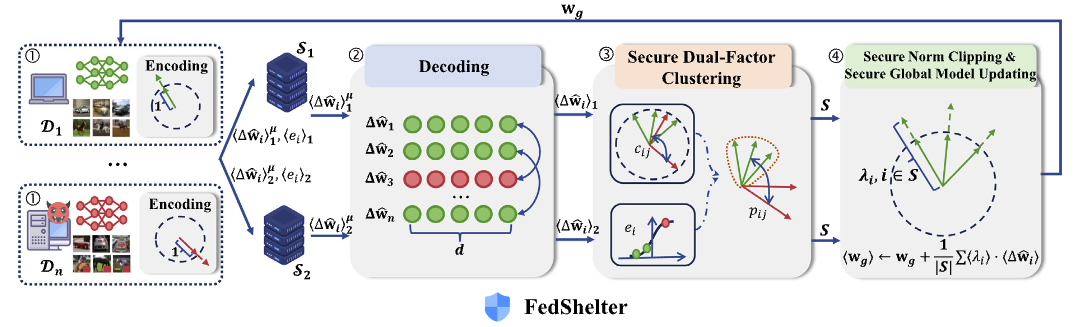
FedShelter: Efficient privacy-preserving federated learning with poisoning resistance for resource-constrained IoT network
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Weizhan Jing, Zhendong Zhao
Computer Networks 2025
CCF-B CORE-A
We propose FedShelter, an efficient privacy-preserving FL framework with poisoning resistance for IoT scenarios. It achieves lightweight Robust SecAgg utilizing Secure Two-party Computation (2PC) and incorporates customized encoding techniques to reduce communication overhead and defend against various poisoning attacks. Compared to state-of-the-art solutions like FLAME (USENIX Security’22) and RoFL (S&P’23), FedShelter offers effective robustness against poisoning attacks while reducing communication by up to 56X and run-time by up to 37X, providing a fast and trustworthy training environment for distributed devices under resource-constrained IoT network.
# secure aggregation # IoT # federated learning # robustness
FedShelter: Efficient privacy-preserving federated learning with poisoning resistance for resource-constrained IoT network
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen†, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong, Weizhan Jing, Zhendong Zhao
Computer Networks 2025 CCF-B CORE-A
We propose FedShelter, an efficient privacy-preserving FL framework with poisoning resistance for IoT scenarios. It achieves lightweight Robust SecAgg utilizing Secure Two-party Computation (2PC) and incorporates customized encoding techniques to reduce communication overhead and defend against various poisoning attacks. Compared to state-of-the-art solutions like FLAME (USENIX Security’22) and RoFL (S&P’23), FedShelter offers effective robustness against poisoning attacks while reducing communication by up to 56X and run-time by up to 37X, providing a fast and trustworthy training environment for distributed devices under resource-constrained IoT network.
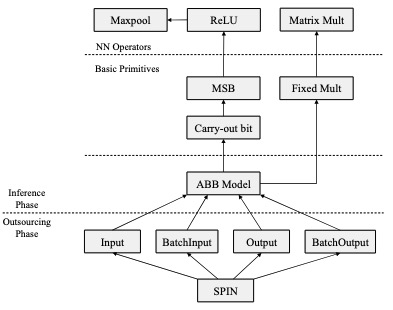
MD-SONIC: Maliciously-Secure Outsourcing Neural Network Inference With Reduced Online Communication
Yansong Zhang, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Qinghui Zhang, Rui Hou, Qiang Liu, Xudong Chen
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025
CCF-A CORE-A
We propose MD-SONIC, an online efficient and maliciously-secure framework for outsourcing NN inference with a dishonest majority. We first construct communication-efficient n-party protocols for the basic primitives such as fixed-point multiplication and most significant bit extraction by combining mask-sharing and TinyOT-sharing with SPD Z2k seamlessly. Then, we build fast secure blocks for the widely used NN operators, including matrix multiplication, ReLU, and Maxpool, on top of our basic primitives. To enable an arbitrary number of users to outsource the secure inference task to n computing servers, we propose a lightweight-client and fast Σ paradigm named SPIN, stemming from zero-knowledge proofs. Our SPIN can be instantiated into a set of efficient outsourcing protocols over multiple algebraic structures (e.g., finite field and ring).
# secure multi-party computation # neural networks # malicious security
MD-SONIC: Maliciously-Secure Outsourcing Neural Network Inference With Reduced Online Communication
Yansong Zhang, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Qinghui Zhang, Rui Hou, Qiang Liu, Xudong Chen
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2025 CCF-A CORE-A
We propose MD-SONIC, an online efficient and maliciously-secure framework for outsourcing NN inference with a dishonest majority. We first construct communication-efficient n-party protocols for the basic primitives such as fixed-point multiplication and most significant bit extraction by combining mask-sharing and TinyOT-sharing with SPD Z2k seamlessly. Then, we build fast secure blocks for the widely used NN operators, including matrix multiplication, ReLU, and Maxpool, on top of our basic primitives. To enable an arbitrary number of users to outsource the secure inference task to n computing servers, we propose a lightweight-client and fast Σ paradigm named SPIN, stemming from zero-knowledge proofs. Our SPIN can be instantiated into a set of efficient outsourcing protocols over multiple algebraic structures (e.g., finite field and ring).
Helix: Scalable Multi-Party Machine Learning Inference against Malicious Adversaries
Yansong Zhang, Xiaojun Chen†, Qinghui Zhang, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong
Cryptology ePrint Archive Under review. 2025
We propose Helix, a scalable framework for maliciously secure PPML in the honest majority setting, aiming to enhance both the scalability and practicality of maliciously secure protocols. In particular, we first report a privacy leakage issue in LXY24 during prefix OR operations and introduce a round-optimized alternative based on a single-round vectorized four-input multiplication protocol. To mitigate the verification burden, we propose a set of lightweight compression protocols by exploiting reusability properties within the computation process, and seamlessly integrate them into existing verification techniques. Building on these enhancements, we further construct a practically-efficient and general n-party computation protocol that serves as the cryptographic foundation for advanced PPML schemes
# secure multi-party computation # secret sharing # malicious security
Helix: Scalable Multi-Party Machine Learning Inference against Malicious Adversaries
Yansong Zhang, Xiaojun Chen†, Qinghui Zhang, Xudong Chen, Ye Dong
Cryptology ePrint ArchiveUnder review. 2025
We propose Helix, a scalable framework for maliciously secure PPML in the honest majority setting, aiming to enhance both the scalability and practicality of maliciously secure protocols. In particular, we first report a privacy leakage issue in LXY24 during prefix OR operations and introduce a round-optimized alternative based on a single-round vectorized four-input multiplication protocol. To mitigate the verification burden, we propose a set of lightweight compression protocols by exploiting reusability properties within the computation process, and seamlessly integrate them into existing verification techniques. Building on these enhancements, we further construct a practically-efficient and general n-party computation protocol that serves as the cryptographic foundation for advanced PPML schemes
Generative AI for internet of things security: Challenges and opportunities
Yan Lin Aung†, Ivan Christian, Ye Dong, Xiaodong Ye, Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Jianying Zhou
arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.08886 Under review. 2025
Survey
This work delves into an examination of the state-of-the-art literature and practical applications on how GenAI could improve and be applied in the security landscape of IoT. Our investigation aims to map the current state of GenAI implementation within IoT security, exploring their potential to fortify security measures further. Through the compilation, synthesis, and analysis of the latest advancements in GenAI technologies applied to IoT, this paper not only introduces fresh insights into the field, but also lays the groundwork for future research directions. It explains the prevailing challenges within IoT security, discusses the effectiveness of GenAI in addressing these issues, and identifies significant research gaps through MITRE Mitigations. Accompanied with three case studies, we provide a comprehensive overview of the progress and future prospects of GenAI applications in IoT security. This study serves as a foundational resource to improve IoT security through the innovative application of GenAI, thus contributing to the broader discourse on IoT security and technology integration.
# Generative AI # IoT
Generative AI for internet of things security: Challenges and opportunities
Yan Lin Aung†, Ivan Christian, Ye Dong, Xiaodong Ye, Sudipta Chattopadhyay, Jianying Zhou
arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.08886Under review. 2025 Survey
This work delves into an examination of the state-of-the-art literature and practical applications on how GenAI could improve and be applied in the security landscape of IoT. Our investigation aims to map the current state of GenAI implementation within IoT security, exploring their potential to fortify security measures further. Through the compilation, synthesis, and analysis of the latest advancements in GenAI technologies applied to IoT, this paper not only introduces fresh insights into the field, but also lays the groundwork for future research directions. It explains the prevailing challenges within IoT security, discusses the effectiveness of GenAI in addressing these issues, and identifies significant research gaps through MITRE Mitigations. Accompanied with three case studies, we provide a comprehensive overview of the progress and future prospects of GenAI applications in IoT security. This study serves as a foundational resource to improve IoT security through the innovative application of GenAI, thus contributing to the broader discourse on IoT security and technology integration.
2024
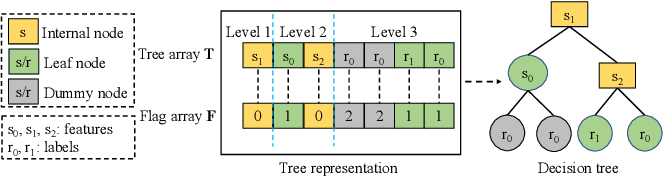
GTree: GPU-Friendly Privacy-preserving Decision Tree Training and Inference
Qifan Wang, Shujie Cui, Lei Zhou†, Ye Dong, Jianli Bai, Yun Sing Koh, Giovanni Russello
IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications 2024
CCF-C CORE-B
GTree is built across 3 parties who jointly perform DT training and inference with GPUs. GTree is secure against semi-honest adversaries, ensuring that no sensitive information is disclosed. GTree offers enhanced security than prior solutions, which only reveal tree depth and data size while prior solutions also leak tree structure. With our oblivious array access, access patterns on GPU are also protected. To harness the full potential of GPUs, we design a novel tree encoding method and craft our MPC protocols into GPU-friendly versions.
# secure multi-party computation # decision tree # GPU
GTree: GPU-Friendly Privacy-preserving Decision Tree Training and Inference
Qifan Wang, Shujie Cui, Lei Zhou†, Ye Dong, Jianli Bai, Yun Sing Koh, Giovanni Russello
IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications 2024 CCF-C CORE-B
GTree is built across 3 parties who jointly perform DT training and inference with GPUs. GTree is secure against semi-honest adversaries, ensuring that no sensitive information is disclosed. GTree offers enhanced security than prior solutions, which only reveal tree depth and data size while prior solutions also leak tree structure. With our oblivious array access, access patterns on GPU are also protected. To harness the full potential of GPUs, we design a novel tree encoding method and craft our MPC protocols into GPU-friendly versions.
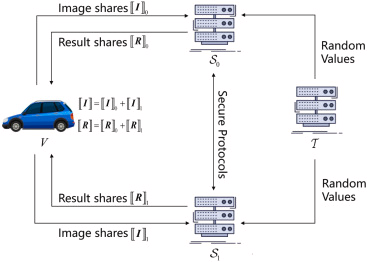
PODI: A Private Object Detection Inference framework for autonomous vehicles
Min Ma, Yu Fu†, Ye Dong, Ximeng Liu, Kai Huang
Knowledge-Based Systems 2024
CCF-C CORE-B
We propose a private object detection inference framework (PODI), which is based on a Faster R-CNN and aims to protect both classification and location privacy. PODI employs additive secret sharing protocols to support collaborative computation between two edge servers. By using efficient protocols such as secure Maxpool, secure array access, and secure exponent, PODI significantly reduces computational and communication overheads.
# privacy # object detection # autonomous vehicles
PODI: A Private Object Detection Inference framework for autonomous vehicles
Min Ma, Yu Fu†, Ye Dong, Ximeng Liu, Kai Huang
Knowledge-Based Systems 2024 CCF-C CORE-B
We propose a private object detection inference framework (PODI), which is based on a Faster R-CNN and aims to protect both classification and location privacy. PODI employs additive secret sharing protocols to support collaborative computation between two edge servers. By using efficient protocols such as secure Maxpool, secure array access, and secure exponent, PODI significantly reduces computational and communication overheads.
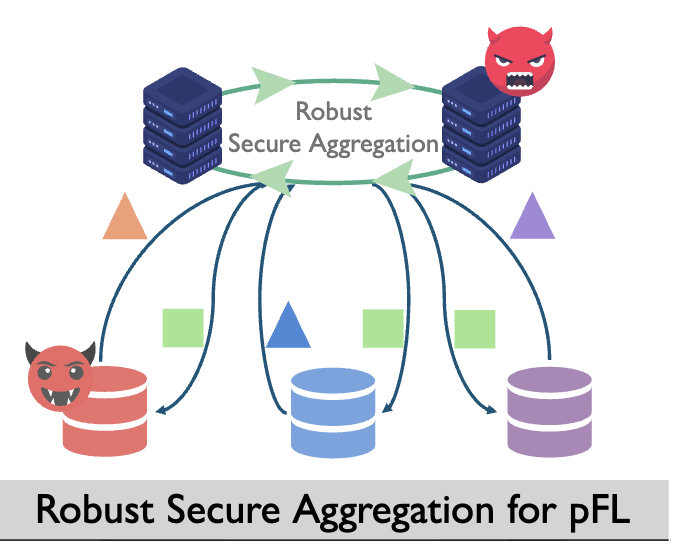
Lightweight Secure Aggregation for Personalized Federated Learning with Backdoor Resistance
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen, Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Yuexin Xuan, Weizhan Jing
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference 2024
CCF-B CORE-A
We propose FLIGHT, a robust secure aggregation method for pFL. It implements a lightweight backdoor detection through a two-stage personalized defense mechanism and ensures privacy preservation using communication-efficient two-party secure computation (2PC) protocols. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets and neural networks validate that FLIGHT decreases run-time up to 64× compared by prior work RoFL (S&P’23), and 42× compared to FLAME (USENIX Security’22).
# secure aggregation # robustness # federated learning
Lightweight Secure Aggregation for Personalized Federated Learning with Backdoor Resistance
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen, Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Yuexin Xuan, Weizhan Jing
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference 2024 CCF-B CORE-A
We propose FLIGHT, a robust secure aggregation method for pFL. It implements a lightweight backdoor detection through a two-stage personalized defense mechanism and ensures privacy preservation using communication-efficient two-party secure computation (2PC) protocols. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets and neural networks validate that FLIGHT decreases run-time up to 64× compared by prior work RoFL (S&P’23), and 42× compared to FLAME (USENIX Security’22).
An Effective Multiple Private Set Intersection
Qiang Liu, Xiaojun Chen†, Weizhan Jing, Ye Dong
EAI International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks 2024
CCF-C CORE-C
We propose Comet,a communication-efficient batch secure three-party inference framework with client-aiding, which achieves semi-honest security in honest majority without collusion between the client and the servers. First, we propose client-aided sharing semantics, which leverages client-generated random values to enhance online communication efficiency. We also design efficient 3PC protocols for neural network operators based on GPU, improving the computational efficiency of both linear and nonlinear layers. Furthermore, we address the tradeoff between communication cost and GPU memory utilization.
# private set intersection # privacy
An Effective Multiple Private Set Intersection
Qiang Liu, Xiaojun Chen†, Weizhan Jing, Ye Dong
EAI International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks 2024 CCF-C CORE-C
We propose Comet,a communication-efficient batch secure three-party inference framework with client-aiding, which achieves semi-honest security in honest majority without collusion between the client and the servers. First, we propose client-aided sharing semantics, which leverages client-generated random values to enhance online communication efficiency. We also design efficient 3PC protocols for neural network operators based on GPU, improving the computational efficiency of both linear and nonlinear layers. Furthermore, we address the tradeoff between communication cost and GPU memory utilization.
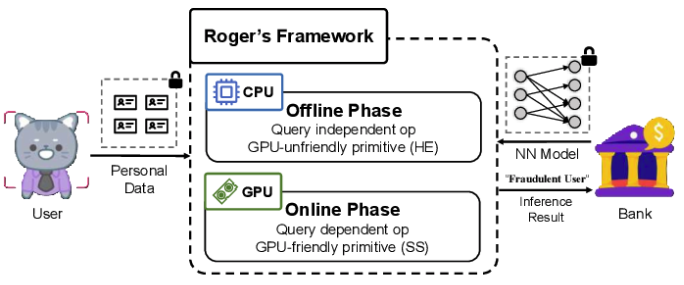
Roger: A Round Optimized GPU-Friendly Secure Inference Framework
Xudong Chen, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Weizhan Jing, Tingyu Fan, Qinghui Zhang
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2024
CCF-C CCF-B
We introduce Roger, a two-party secure inference framework with semi-honest security, designed to support general neural network inference with a reduced number of round complexity. Drawing inspiration from ABY2.0 [3], we propose the Partial-Fix technology, which fixes the share of one participant during the offline phase to improve its computation efficiency. Then, an online communication-free protocol for secure linear layer computation and a constant-round secure comparison protocol are proposed upon Partial-Fix.
# secure multi-party computation # neural network # GPU
Roger: A Round Optimized GPU-Friendly Secure Inference Framework
Xudong Chen, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Weizhan Jing, Tingyu Fan, Qinghui Zhang
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2024 CCF-C CCF-B
We introduce Roger, a two-party secure inference framework with semi-honest security, designed to support general neural network inference with a reduced number of round complexity. Drawing inspiration from ABY2.0 [3], we propose the Partial-Fix technology, which fixes the share of one participant during the offline phase to improve its computation efficiency. Then, an online communication-free protocol for secure linear layer computation and a constant-round secure comparison protocol are proposed upon Partial-Fix.
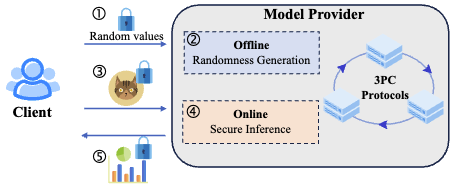
Comet: Communication-Efficient Batch Secure Three-Party Neural Network Inference with Client-Aiding
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Weizhan Jing
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2024
CCF-C CCF-B
We propose Comet,a communication-efficient batch secure three-party inference framework with client-aiding, which achieves semi-honest security in honest majority without collusion between the client and the servers. First, we propose client-aided sharing semantics, which leverages client-generated random values to enhance online communication efficiency. We also design efficient 3PC protocols for neural network operators based on GPU, improving the computational efficiency of both linear and nonlinear layers. Furthermore, we address the tradeoff between communication cost and GPU memory utilization.
# secure multi-party computation # neural network # GPU
Comet: Communication-Efficient Batch Secure Three-Party Neural Network Inference with Client-Aiding
Tingyu Fan, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Xudong Chen, Weizhan Jing
IEEE International Conference on Communications 2024 CCF-C CCF-B
We propose Comet,a communication-efficient batch secure three-party inference framework with client-aiding, which achieves semi-honest security in honest majority without collusion between the client and the servers. First, we propose client-aided sharing semantics, which leverages client-generated random values to enhance online communication efficiency. We also design efficient 3PC protocols for neural network operators based on GPU, improving the computational efficiency of both linear and nonlinear layers. Furthermore, we address the tradeoff between communication cost and GPU memory utilization.
2023
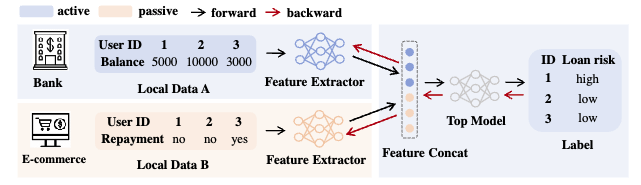
Practical and General Backdoor Attacks Against Vertical Federated Learning
Yuexin Xuan, Xiaojun Chen†, Zhendong Zhao, Bisheng Tang, Ye Dong
Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases 2023
CCF-B CORE-A
We propose BadVFL, a novel and practical approach to inject backdoor triggers into victim models without label information. BadVFL mainly consists of two key steps. First, to address the challenge of attackers having no knowledge of labels, we introduce a SDD module that can trace data categories based on gradients. Second, we propose a SDP module that can improve the attack’s effectiveness by enhancing the decision dependency between the trigger and attack target.
# federated learning # backdoor
Practical and General Backdoor Attacks Against Vertical Federated Learning
Yuexin Xuan, Xiaojun Chen†, Zhendong Zhao, Bisheng Tang, Ye Dong
Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases 2023 CCF-B CORE-A
We propose BadVFL, a novel and practical approach to inject backdoor triggers into victim models without label information. BadVFL mainly consists of two key steps. First, to address the challenge of attackers having no knowledge of labels, we introduce a SDD module that can trace data categories based on gradients. Second, we propose a SDP module that can improve the attack’s effectiveness by enhancing the decision dependency between the trigger and attack target.
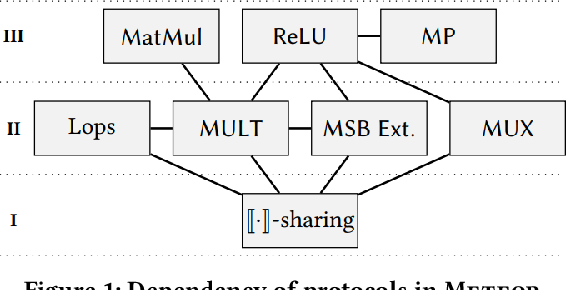
Meteor: Improved Secure 3-Party Neural Network Inference with Reducing Online Communication Costs
Ye Dong, Chen Xiaojun†, Weizhan Jing, Li Kaiyun, Weiping Wang
ACM Web Conference (WWW) 2023
CCF-A CORE-A*
[TL;DR] [Paper] [Code] [Video] [Hackthon 1st Prize]
The main contributions of Meteor are two-fold: i) We propose a new and improved 3-party secret sharing scheme stemming from the linearity of replicated secret sharing, and design efficient protocols for the basic cryptographic primitives, including linear operations, multiplication, most significant bit extraction, and multiplexer. ii) Furthermore, we build efficient and secure blocks for the widely used neural network operators such as Matrix Multiplication, ReLU, and Maxpool, along with exploiting several specific optimizations for better efficiency. Our total communication with the setup phase is a little larger than SecureNN (PoPETs’19) and Falcon (PoPETs’21), two state-of-the-art solutions, but the gap is not significant when the online phase must be optimized as a priority.
# secure multi-party computation # neural network # masked secret sharing
Meteor: Improved Secure 3-Party Neural Network Inference with Reducing Online Communication Costs
Ye Dong, Chen Xiaojun†, Weizhan Jing, Li Kaiyun, Weiping Wang
ACM Web Conference (WWW) 2023 CCF-A CORE-A*
The main contributions of Meteor are two-fold: i) We propose a new and improved 3-party secret sharing scheme stemming from the linearity of replicated secret sharing, and design efficient protocols for the basic cryptographic primitives, including linear operations, multiplication, most significant bit extraction, and multiplexer. ii) Furthermore, we build efficient and secure blocks for the widely used neural network operators such as Matrix Multiplication, ReLU, and Maxpool, along with exploiting several specific optimizations for better efficiency. Our total communication with the setup phase is a little larger than SecureNN (PoPETs’19) and Falcon (PoPETs’21), two state-of-the-art solutions, but the gap is not significant when the online phase must be optimized as a priority.
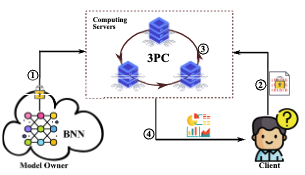
FlexBNN: fast private binary neural network inference with flexible bit-width
Ye Dong, Chen Xiaojun†, Xiangfu Song, Li Kaiyun
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2023
CCF-A CORE-A
In FlexBNN, we propose to employ flexible and small bit-width equipped with a seamless bit-width conversion method and design several specific optimizations towards the basic operations: i) We propose bit-width determination methods for Matrix Multiplication and Sign-based Activation function. ii) We integrate Batch Normalization and Max-Pooling into the Sign-based Activation function for better efficiency. iii) More importantly, we achieve seamless bit-width conversion within the Sign-based Activation function with no additional cost. Extensive experiments illustrate that FlexBNN outperforms state-of-the-art solutions in communication, run-time, and scalability.
# secure multi-party computation # binary neural network
FlexBNN: fast private binary neural network inference with flexible bit-width
Ye Dong, Chen Xiaojun†, Xiangfu Song, Li Kaiyun
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2023 CCF-A CORE-A
In FlexBNN, we propose to employ flexible and small bit-width equipped with a seamless bit-width conversion method and design several specific optimizations towards the basic operations: i) We propose bit-width determination methods for Matrix Multiplication and Sign-based Activation function. ii) We integrate Batch Normalization and Max-Pooling into the Sign-based Activation function for better efficiency. iii) More importantly, we achieve seamless bit-width conversion within the Sign-based Activation function with no additional cost. Extensive experiments illustrate that FlexBNN outperforms state-of-the-art solutions in communication, run-time, and scalability.
2022

ABNN2: secure two-party arbitrary-bitwidth quantized neural network predictions
Liyan Shen†, Ye Dong, Binxing Fang, Jinqiao Shi, Xuebin Wang, Shengli Pan, Ruisheng Shi
ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference 2022
CCF-A CORE-A
We utilize the advantages of quantized neural network (QNN) and MPC to present ABNN2, a practical secure two-party framework that can realize arbitrary-bitwidth quantized neural network predictions. Concretely, we propose an efficient and novel matrix multiplication protocol based on 1-out-of-N OT extension and optimize the the protocol through a parallel scheme. In addition, we design optimized protocol for the ReLU function.
# secure multi-party computation # quantized neural networks
ABNN2: secure two-party arbitrary-bitwidth quantized neural network predictions
Liyan Shen†, Ye Dong, Binxing Fang, Jinqiao Shi, Xuebin Wang, Shengli Pan, Ruisheng Shi
ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference 2022 CCF-A CORE-A
We utilize the advantages of quantized neural network (QNN) and MPC to present ABNN2, a practical secure two-party framework that can realize arbitrary-bitwidth quantized neural network predictions. Concretely, we propose an efficient and novel matrix multiplication protocol based on 1-out-of-N OT extension and optimize the the protocol through a parallel scheme. In addition, we design optimized protocol for the ReLU function.
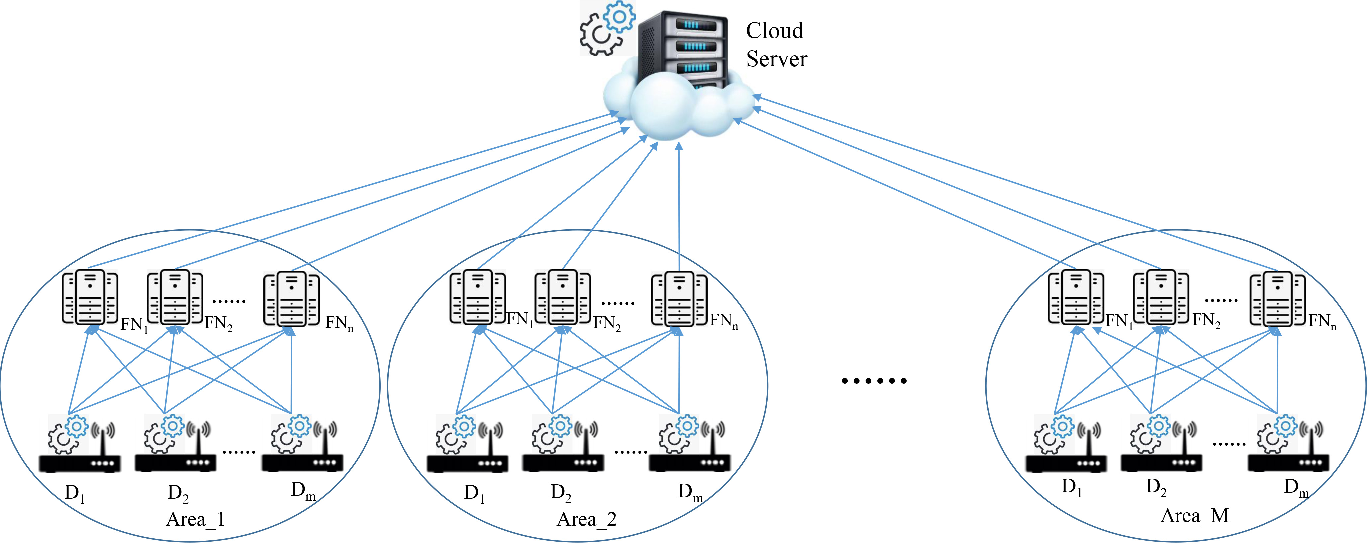
Distributed fog computing and federated-learning-enabled secure aggregation for IoT devices
Yiran Liu, Ye Dong, Hao Wang, Han Jiang, Qiuliang Xu†
IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022
CCF-C
We propose a secure aggregation protocol based on efficient additive secret sharing in the fog-computing (FC) setting. As the secure aggregation is performed frequently in the training process of FL, the protocol should have low communication and computation overhead. First, we use a fog node (FN) as an intermediate processing unit to provide local services which can assist the cloud server aggregated the sum during the training process. Second, we design a light Request-then-Broadcast method to ensure our protocol has the robustness to dropped-out clients. Our protocol also provides two simple new client selection methods. The security and performance of our protocol are analyzed and compared with existed schemes.
# fog compting # federated learning # secure aggregation # IoT
Distributed fog computing and federated-learning-enabled secure aggregation for IoT devices
Yiran Liu, Ye Dong, Hao Wang, Han Jiang, Qiuliang Xu†
IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022 CCF-C
We propose a secure aggregation protocol based on efficient additive secret sharing in the fog-computing (FC) setting. As the secure aggregation is performed frequently in the training process of FL, the protocol should have low communication and computation overhead. First, we use a fog node (FN) as an intermediate processing unit to provide local services which can assist the cloud server aggregated the sum during the training process. Second, we design a light Request-then-Broadcast method to ensure our protocol has the robustness to dropped-out clients. Our protocol also provides two simple new client selection methods. The security and performance of our protocol are analyzed and compared with existed schemes.
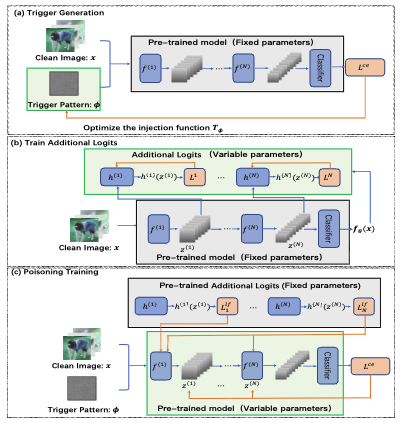
Defeat: Deep hidden feature backdoor attacks by imperceptible perturbation and latent representation constraints
Zhendong Zhao, Xiaojun Chen†, Yuexin Xuan, Ye Dong, Dakui Wang, Kaitai Liang
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2022
CCF-A CORE-A*
# backdoor # deep learning
Defeat: Deep hidden feature backdoor attacks by imperceptible perturbation and latent representation constraints
Zhendong Zhao, Xiaojun Chen†, Yuexin Xuan, Ye Dong, Dakui Wang, Kaitai Liang
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2022 CCF-A CORE-A*
We propose a novel and stealthy backdoor attack - DEFEAT. It poisons the clean data using adaptive imperceptible perturbation and restricts latent representation during training process to strengthen our attack's stealthiness and resistance to defense algorithms.We conduct extensive experiments on multiple image classifiers using real-world datasets to demonstrate that our attack can 1) hold against the state-of-the-art defenses, 2) deceive the victim model with high attack success without jeopardizing model utility, and 3) provide practical stealthiness on image data.
2021
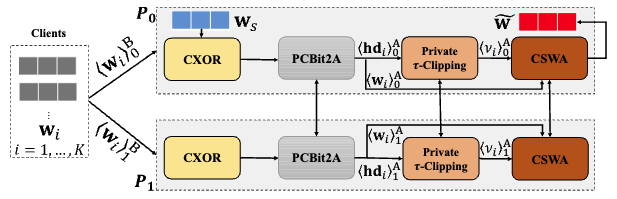
FLOD: Oblivious Defender for Private Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning with Dishonest-Majority
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Kaiyun Li, Dakui Wang, Shuai Zeng
European Symposium on Research in Computer Security 2021
CCF-B CORE-A
We present a novel oblivious defender for private Byzantine-robust FL in dishonest-majority setting. Basically, we propose a novel Hamming distance-based aggregation method to resist Byzantine attacks using a small root-dataset and server-model for bootstrapping trust. Furthermore, we employ two non-colluding servers and use additive homomorphic encryption and secure two-party computation (2PC) primitives to construct efficient privacy-preserving building blocks for secure aggregation, in which we propose two novel in-depth variants of Beaver Multiplication triples (MT) to reduce the overhead of Bit to Arithmetic conversion and vector weighted sum aggregation significantly.
# federated learning # secure aggregation # robustness
FLOD: Oblivious Defender for Private Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning with Dishonest-Majority
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Kaiyun Li, Dakui Wang, Shuai Zeng
European Symposium on Research in Computer Security 2021 CCF-B CORE-A
We present a novel oblivious defender for private Byzantine-robust FL in dishonest-majority setting. Basically, we propose a novel Hamming distance-based aggregation method to resist Byzantine attacks using a small root-dataset and server-model for bootstrapping trust. Furthermore, we employ two non-colluding servers and use additive homomorphic encryption and secure two-party computation (2PC) primitives to construct efficient privacy-preserving building blocks for secure aggregation, in which we propose two novel in-depth variants of Beaver Multiplication triples (MT) to reduce the overhead of Bit to Arithmetic conversion and vector weighted sum aggregation significantly.
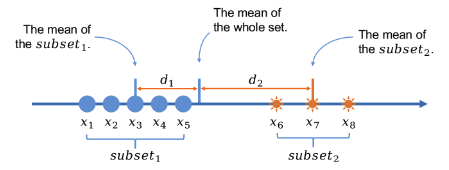
Efficient Byzantine-Resilient Stochastic Gradient Descent
Kaiyun Li, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Peng Zhang, Dakui Wang, Shuai Zeng
FTL-Workshop@IJCAI 2021
We propose a new Byzantine-resilient stochastic gradient descent algorithm (BrSGD for short) which is provably robust against Byzantine failures. BrSGD obtains the optimal statistical performance and efficient computation simultaneously. In particular, BrSGD can achieve an order-optimal statistical error rate for strongly convex loss functions. The computation complexity of BrSGD is O(md), where d is the model dimension and m is the number of machines. Experimental results show that BrSGD can obtain competitive results compared with non-Byzantine machines in terms of effectiveness and convergence.
# federated learning # robustness
Efficient Byzantine-Resilient Stochastic Gradient Descent
Kaiyun Li, Xiaojun Chen†, Ye Dong, Peng Zhang, Dakui Wang, Shuai Zeng
FTL-Workshop@IJCAI 2021
We propose a new Byzantine-resilient stochastic gradient descent algorithm (BrSGD for short) which is provably robust against Byzantine failures. BrSGD obtains the optimal statistical performance and efficient computation simultaneously. In particular, BrSGD can achieve an order-optimal statistical error rate for strongly convex loss functions. The computation complexity of BrSGD is O(md), where d is the model dimension and m is the number of machines. Experimental results show that BrSGD can obtain competitive results compared with non-Byzantine machines in terms of effectiveness and convergence.
2020
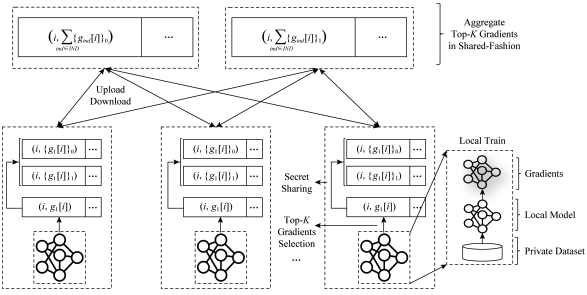
Efficient and secure federated learning based on secret sharing and gradients selection
Ye Dong, Wei Hou, Xiaojun Chen†, Dakui Wang
Journal of Compute Research Development 2020
We combine secret sharing with Top-K gradients selection to design efficient and secure federated learning protocols, so that we can cut down the communication overheads and improve the efficiency during the training phase while guaranteeing the users privacy and data security. Also, we propose an efficient method to construct message authentication code (MAC) to verify the validity of the aggregated results from the servers. And the communication overheads introduced by the MAC is small and independent of the number of shared gradients. Besides, we implement a prototype system. Compared with the plaintext training, on the one hand, our secure techniques introduce small additional overheads in communication and computation; On the other hand, we achieve the same level of accuracy as the plaintext training.
# federated learning # secure aggregation # Top-k gradients selection
Efficient and secure federated learning based on secret sharing and gradients selection
Ye Dong, Wei Hou, Xiaojun Chen†, Dakui Wang
Journal of Compute Research Development 2020
We combine secret sharing with Top-K gradients selection to design efficient and secure federated learning protocols, so that we can cut down the communication overheads and improve the efficiency during the training phase while guaranteeing the users privacy and data security. Also, we propose an efficient method to construct message authentication code (MAC) to verify the validity of the aggregated results from the servers. And the communication overheads introduced by the MAC is small and independent of the number of shared gradients. Besides, we implement a prototype system. Compared with the plaintext training, on the one hand, our secure techniques introduce small additional overheads in communication and computation; On the other hand, we achieve the same level of accuracy as the plaintext training.

An efficient 3-party framework for privacy-preserving neural network inference
Liyan Shen, Xiaojun Chen†, Jinqiao Shi, Ye Dong, Binxing Fang
European Symposium on Research in Computer Security 2020
CCF-B CORE-A
We focus on the efficiency problem of privacy-preserving neural network inference and propose novel 3-party secure protocols to implement amounts of nonlinear activation functions such as ReLU and Sigmod, etc.
# secure multi-party computation # neural network
An efficient 3-party framework for privacy-preserving neural network inference
Liyan Shen, Xiaojun Chen†, Jinqiao Shi, Ye Dong, Binxing Fang
European Symposium on Research in Computer Security 2020 CCF-B CORE-A
We focus on the efficiency problem of privacy-preserving neural network inference and propose novel 3-party secure protocols to implement amounts of nonlinear activation functions such as ReLU and Sigmod, etc.
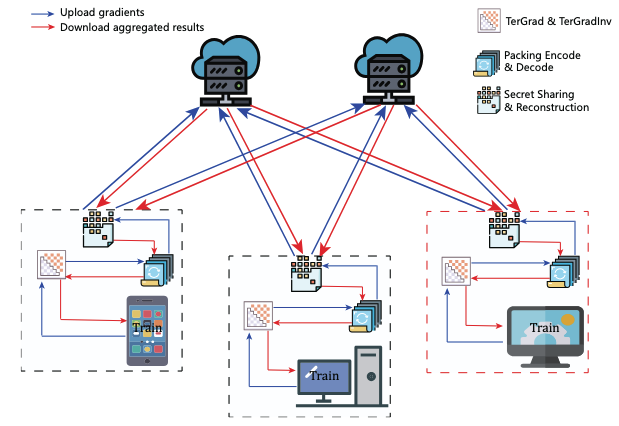
EaSTFLy: Efficient and secure ternary federated learning
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Liyan Shen, Dakui Wang
Computer & Security 2020
CCF-B
In this paper, firstly, we analyze the privacy leakages of TernGrad. Then, we present our solution-EaSTFLy to solve the privacy issue. More concretely, in EaSTFLy, we combine TernGrad with secret sharing and homomorphic encryption to design our privacy-preserving protocols against semi-honest adversary. In addition, we optimize our protocols via SIMD.
# federated learning # secure aggregation # ternary quanized gradients
EaSTFLy: Efficient and secure ternary federated learning
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Liyan Shen, Dakui Wang
Computer & Security 2020 CCF-B
In this paper, firstly, we analyze the privacy leakages of TernGrad. Then, we present our solution-EaSTFLy to solve the privacy issue. More concretely, in EaSTFLy, we combine TernGrad with secret sharing and homomorphic encryption to design our privacy-preserving protocols against semi-honest adversary. In addition, we optimize our protocols via SIMD.
2019
Privacy-preserving distributed machine learning based on secret sharing
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Liyan Shen, Dakui Wang
International Conference on Information and Communications Security 2019
CCF-C CORE-C
we join secret sharing to distributed machine learning to achieve reliable performance, accuracy, and high-level security. Next, we design, implement, and evaluate a practical system to jointly learn an accurate model under semi-honest and servers-only malicious adversary security, respectively. And the experiments show our protocols achieve the best overall performance as well.
# secure aggregation # federated learning
Privacy-preserving distributed machine learning based on secret sharing
Ye Dong, Xiaojun Chen†, Liyan Shen, Dakui Wang
International Conference on Information and Communications Security 2019 CCF-C CORE-C
we join secret sharing to distributed machine learning to achieve reliable performance, accuracy, and high-level security. Next, we design, implement, and evaluate a practical system to jointly learn an accurate model under semi-honest and servers-only malicious adversary security, respectively. And the experiments show our protocols achieve the best overall performance as well.
2018
Efficient and Private Set Intersection of Human Genomes
Liyan Shen, Xiaojun Chen†, Dakui Wang, Binxing Fang, Ye Dong
IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine 2018
CCF-B
We mainly focus on efficient and privacy-preserving set intersection protocol of human genomes. It makes the paternity and ancestry testing perform safely, without disclosing any additional individual's genomic information. Experimental results demonstrate that proposed techniques have better performance.
# private set intersection # human genomes
Efficient and Private Set Intersection of Human Genomes
Liyan Shen, Xiaojun Chen†, Dakui Wang, Binxing Fang, Ye Dong
IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine 2018 CCF-B
We mainly focus on efficient and privacy-preserving set intersection protocol of human genomes. It makes the paternity and ancestry testing perform safely, without disclosing any additional individual's genomic information. Experimental results demonstrate that proposed techniques have better performance.